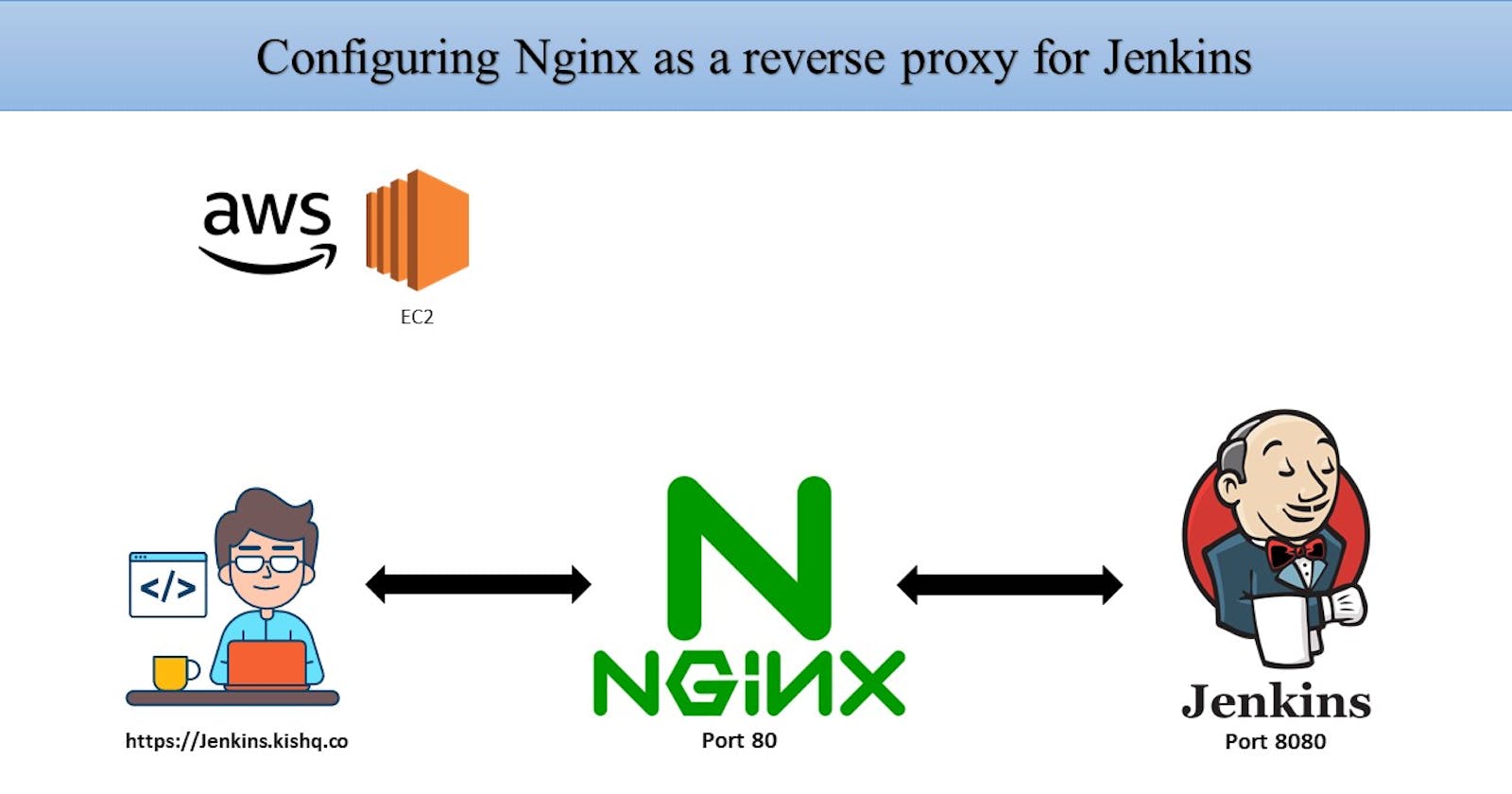
Reverse Proxy
A reverse proxy is a server that sits between clients and servers. It receives requests from clients and forwards them to the appropriate server. This can be used to improve performance, security, and reliability.
Here are some of the benefits of using a reverse proxy:
Performance: A reverse proxy can improve performance by caching content and serving it from its own memory. This can reduce the load on the back-end servers.
Security: A reverse proxy can improve security by acting as a firewall between clients and servers. It can also be used to implement SSL/TLS encryption, which can help to protect sensitive data.
Reliability: A reverse proxy can improve reliability by providing a single point of failure. If one of the back-end servers goes down, the reverse proxy can continue to serve requests from the other servers.
There are many different reverse proxy servers available, including Nginx, Apache, and HAProxy. The best reverse proxy server for you will depend on your specific needs.
Here are some of the most popular reverse proxy servers:
Nginx: Nginx is a high-performance, lightweight web server that is also a popular reverse proxy server. It is easy to configure and can be used to proxy requests for a variety of protocols, including HTTP, HTTPS, and WebSockets.
Apache: Apache is a popular web server that can also be used as a reverse proxy server. It is more complex to configure than Nginx, but it offers a wider range of features.
HAProxy: HAProxy is a high-performance, load balancing reverse proxy server. It is designed to handle large numbers of requests and can be used to proxy requests for a variety of protocols, including HTTP, HTTPS, and WebSockets.
Nginx
Nginx (engine x) is a web server software that can also be used as a reverse proxy, load balancer, mail proxy and HTTP cache. The software was created by Igor Sysoev and publicly released in 2004. Nginx is free and open-source software, released under the terms of the 2-clause BSD license.
Nginx is a popular choice for web servers because it is fast, efficient, and scalable. It is also relatively easy to configure and manage. Nginx is used by many large websites, including Netflix, Airbnb, and Dropbox.
Here are some of the benefits of using Nginx:
Performance: Nginx is a very fast web server. It can handle a large number of concurrent requests without slowing down.
Efficiency: Nginx is a very efficient web server. It uses less memory and CPU resources than other web servers.
Scalability: Nginx is a very scalable web server. It can be easily scaled to handle a large number of requests.
Ease of configuration: Nginx is very easy to configure. The configuration files are easy to read and understand.
Security: Nginx is a very secure web server. It comes with a number of security features, including SSL/TLS support and rate limiting.
If you are looking for a fast, efficient, and scalable web server, Nginx is a great option. It is easy to configure and manage, and it comes with a number of security features.
Jenkins
Jenkins is a free and open-source automation server that helps you automate the parts of software development related to building, testing, and deploying, facilitating continuous integration and continuous delivery.
Jenkins is used by a wide variety of organizations, including large enterprises, small businesses, and open source projects. It is a popular choice for automation because it is easy to use, extensible, and scalable.
Jenkins can be used to automate a wide variety of tasks, including:
Building software
Running tests
Deploying software
Managing releases
Monitoring performance
Reporting on results
Jenkins is a powerful tool that can help you improve the quality and efficiency of your software development process. If you are looking for a way to automate your software development, Jenkins is a great option.
Here are some of the benefits of using Jenkins:
Ease of use: Jenkins is easy to use, even for beginners. The user interface is intuitive and the documentation is comprehensive.
Extensibility: Jenkins is highly extensible. There are thousands of plugins available that can be used to add new features and functionality.
Scalability: Jenkins is scalable. It can be used to automate the development of large and complex software projects.
Community: Jenkins has a large and active community. There are many resources available to help you get started with Jenkins, including tutorials, documentation, and support forums.
If you are looking for a way to automate your software development, Jenkins is a great option. It is easy to use, extensible, scalable, and has a large and active community.
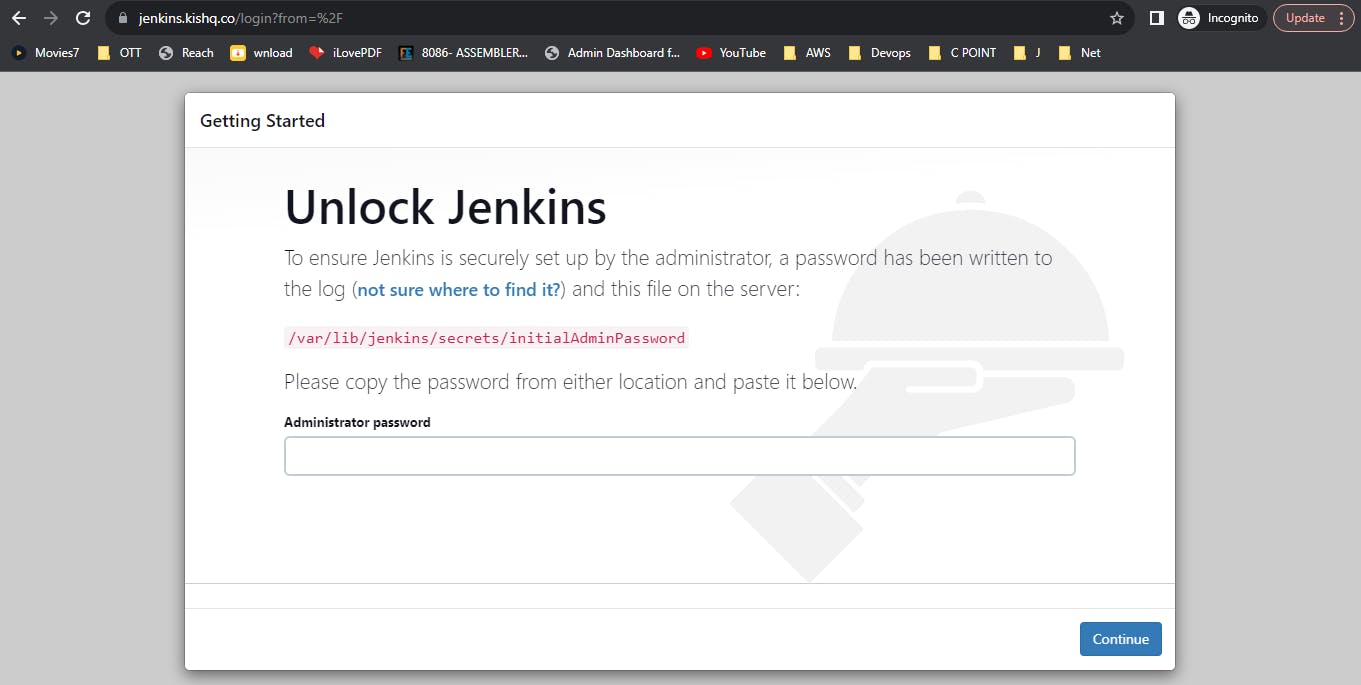
Configuring Nginx as Reverse Proxy for Jenkins
Go to the AWS Management Console and sign in to your account.
In the navigation pane, choose EC2.
In the Launch Instance wizard, choose an AMI (Amazon Machine Image).
Choose an instance type.
Create or Choose the Key Pair.
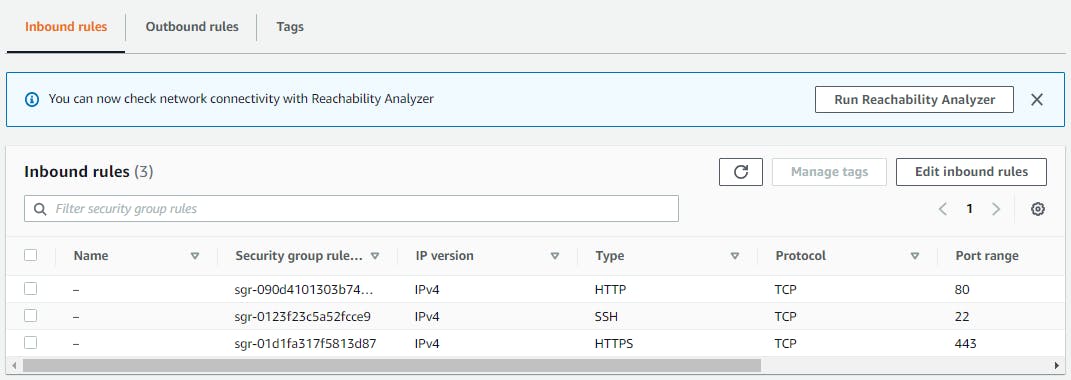
Configure the Security Group with ports 22,80,443
Review your instance settings and launch your instance.
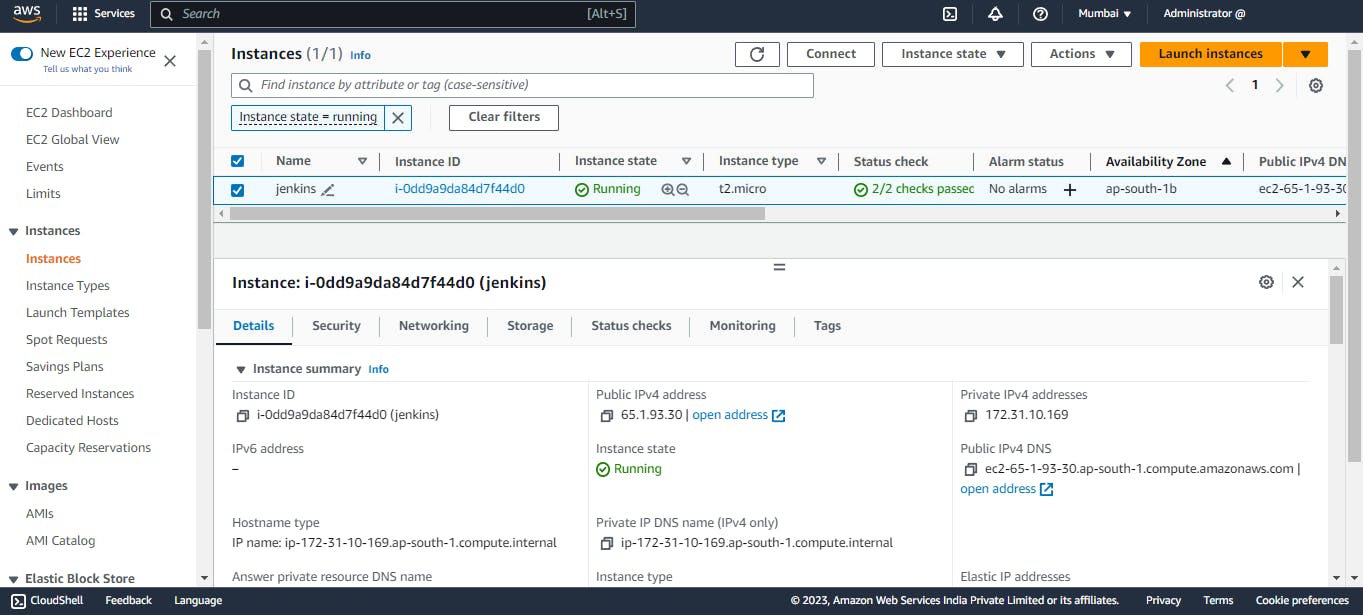
Connect to your instance with IP address and key pair using any tool like Mobaxterm or Putty.
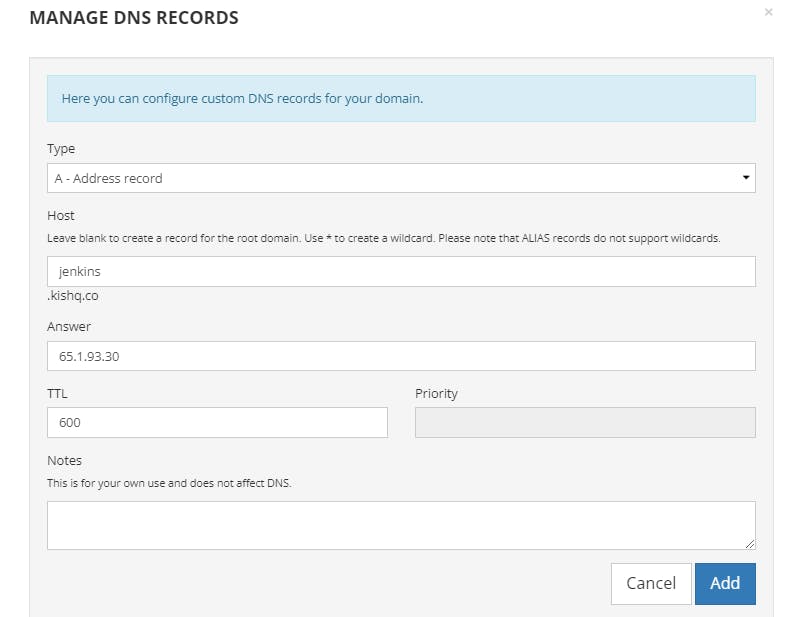
Configuring Domain (DNS)
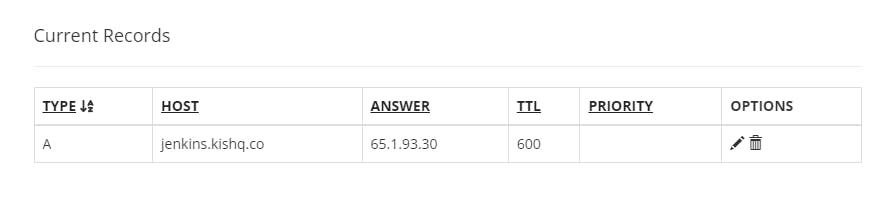
Go to your Domain name registrar, navigate DNS Records and match your instance IP address to the subdomain, in my case I have a domain "kishq.co", so i created a subdomain jenkins.kishq.co and matched it with the instance ip address.
Installing Jenkins
wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/jenkins.repo \
https://pkg.jenkins.io/redhat-stable/jenkins.repo
rpm --import https://pkg.jenkins.io/redhat-stable/jenkins.io-2023.key$ yum upgrade -y
# Add required dependencies for the jenkins package
amazon-linux-extras install java-openjdk11 -y
yum install jenkins -y
systemctl start jenkins.service
Installing Nginx
amazon-linux-extras install nginx1 -y
systemctl start nginx.service
Navigate to nginx configuration directory and delete the server details from the nginx.conf file. The edited nginx.conf file should look like the below image.
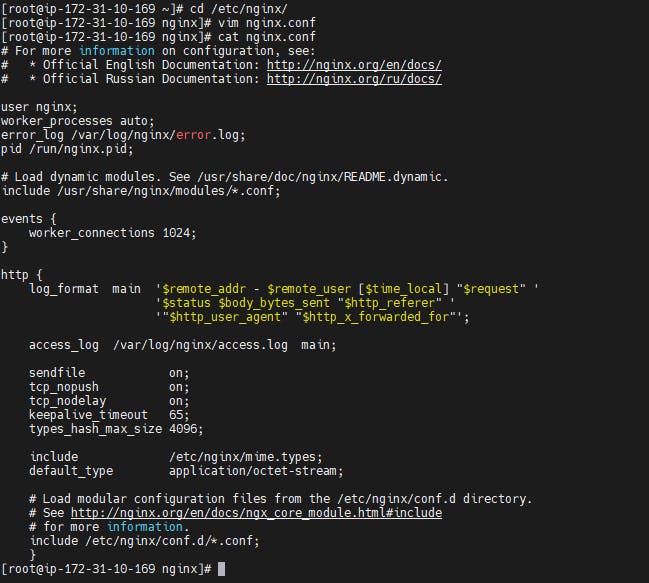
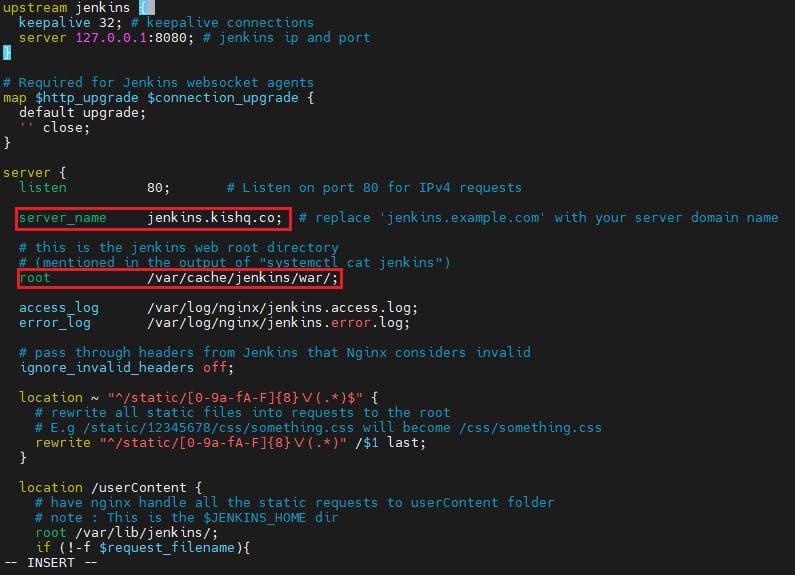
Now navigate to /etc/nginx/conf.d and create jenkins.conf file and copy the below content, edit the configuration and save the jenkins.conf file.
upstream jenkins {
keepalive 32; # keepalive connections
server 127.0.0.1:8080; # jenkins ip and port
}
# Required for Jenkins websocket agents
map $http_upgrade $connection_upgrade {
default upgrade;
'' close;
}
server {
listen 80; # Listen on port 80 for IPv4 requests
server_name jenkins.example.com; # replace 'jenkins.example.com' with your server domain name
# this is the jenkins web root directory
# (mentioned in the output of "systemctl cat jenkins")
root /var/run/jenkins/war/;
access_log /var/log/nginx/jenkins.access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/jenkins.error.log;
# pass through headers from Jenkins that Nginx considers invalid
ignore_invalid_headers off;
location ~ "^/static/[0-9a-fA-F]{8}\/(.*)$" {
# rewrite all static files into requests to the root
# E.g /static/12345678/css/something.css will become /css/something.css
rewrite "^/static/[0-9a-fA-F]{8}\/(.*)" /$1 last;
}
location /userContent {
# have nginx handle all the static requests to userContent folder
# note : This is the $JENKINS_HOME dir
root /var/lib/jenkins/;
if (!-f $request_filename){
# this file does not exist, might be a directory or a /**view** url
rewrite (.*) /$1 last;
break;
}
sendfile on;
}
location / {
sendfile off;
proxy_pass http://jenkins;
proxy_redirect default;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
# Required for Jenkins websocket agents
proxy_set_header Connection $connection_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
proxy_max_temp_file_size 0;
#this is the maximum upload size
client_max_body_size 10m;
client_body_buffer_size 128k;
proxy_connect_timeout 90;
proxy_send_timeout 90;
proxy_read_timeout 90;
proxy_buffering off;
proxy_request_buffering off; # Required for HTTP CLI commands
proxy_set_header Connection ""; # Clear for keepalive
}
}
- Change
server_name jenkins.example.com;toserver_name jenkins.kishq.co
where 'kishq.co' is my domain
- Change
root /var/run/jenkins/war/;toroot /var/cache/jenkins/war/;
nginx -t
nginx -s reload
use nginx -T to see nginx configuration
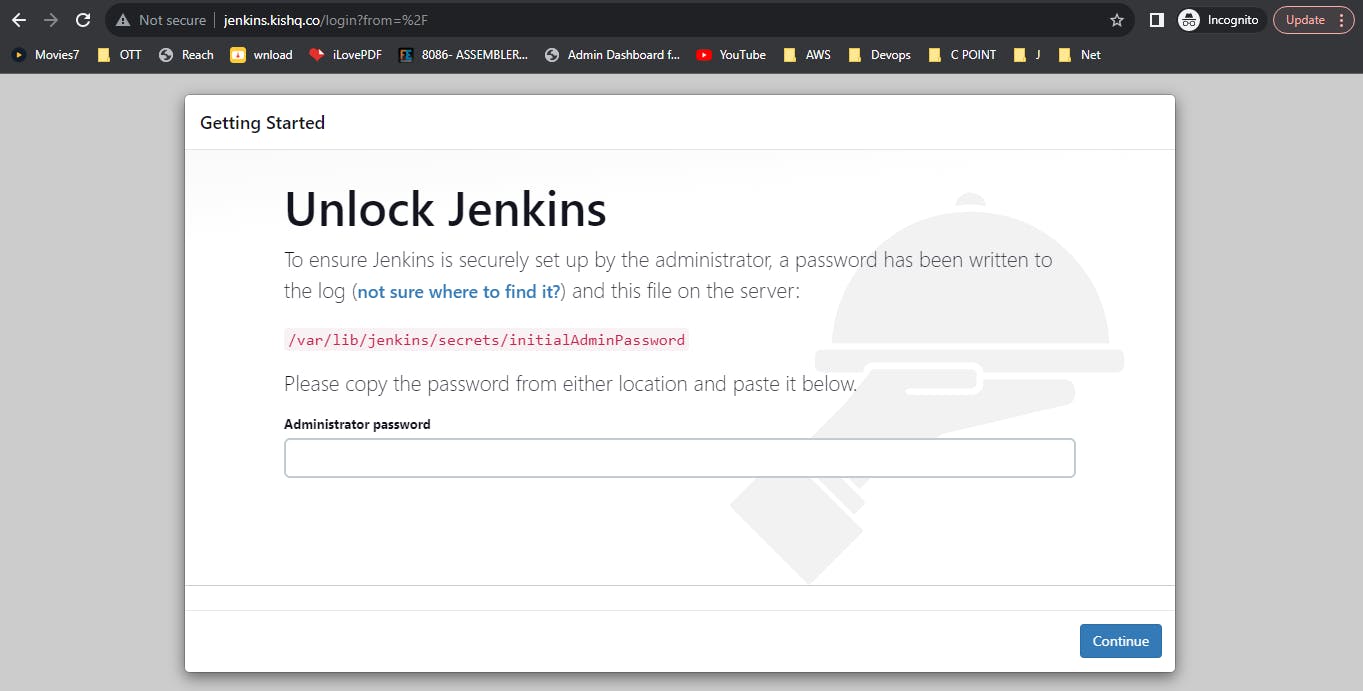
Now go to any browser and search "jenkins.your_domain" e.x: "jenkins.kishq.co"
Now install 'certbot' for SSL Certificates
amazon-linux-extras install epel -y
yum install certbot -y
yum install python-certbot-nginx -y
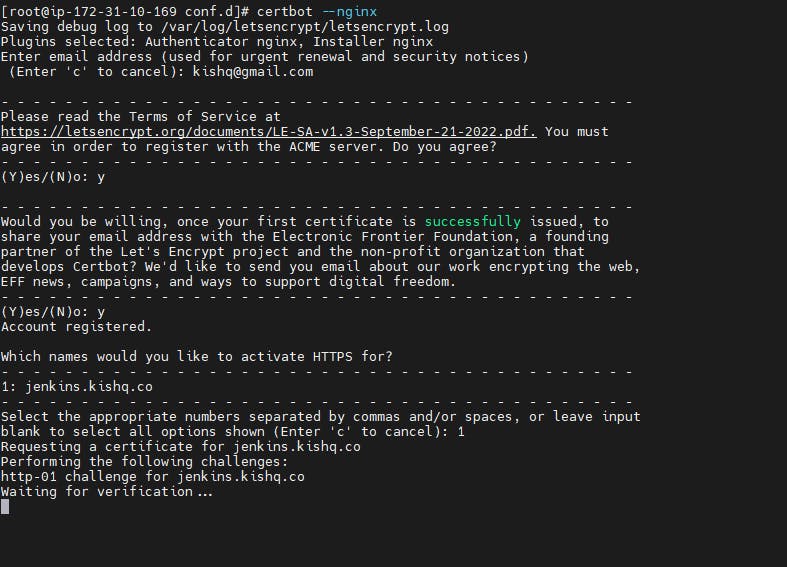
To install SSL for the subdomain 'jenkins.kishq.co' execute the below command and give the email and select the domain.
certbot --nginx
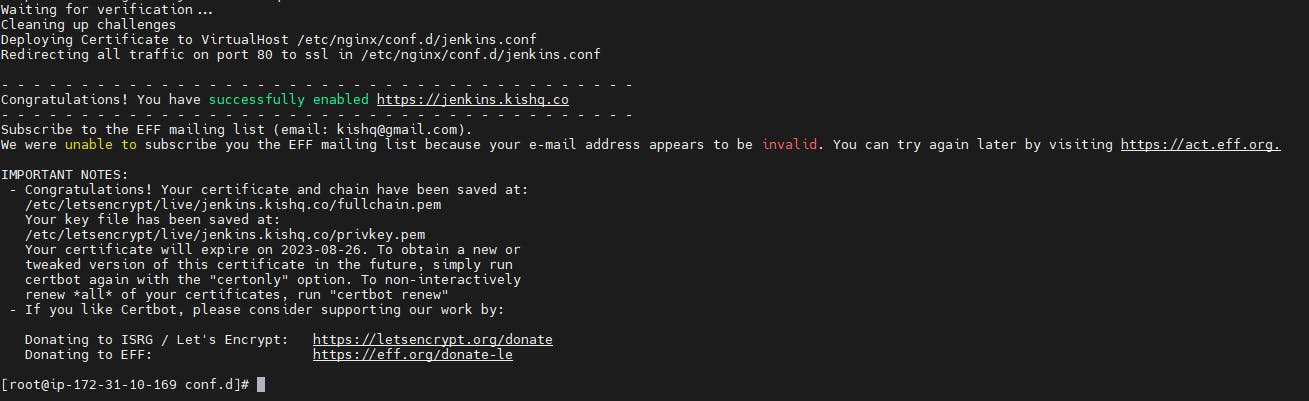
Now go and refresh the page, you can see that 'jenkins.kishq.co' was SSL Encrytped